In the United States alone, 16.5 million people have atopic dermatitis, with many living with moderate to severe symptoms. In the past, atopic dermatitis was considered to be a condition that only affected children, characterized by symptoms starting before the teen years and then gradually improving. In recent years, however, researchers have realized that many adults also live with the condition — without reaching out for help.
Atopic dermatitis is allergic in nature, making its causes and symptoms different from other skin conditions. Fortunately, medications and other treatment options can help you get relief from the symptoms. Here is everything you need to know about atopic dermatitis, its symptoms and causes, and what treatment options you can use for help.
What is atopic dermatitis?
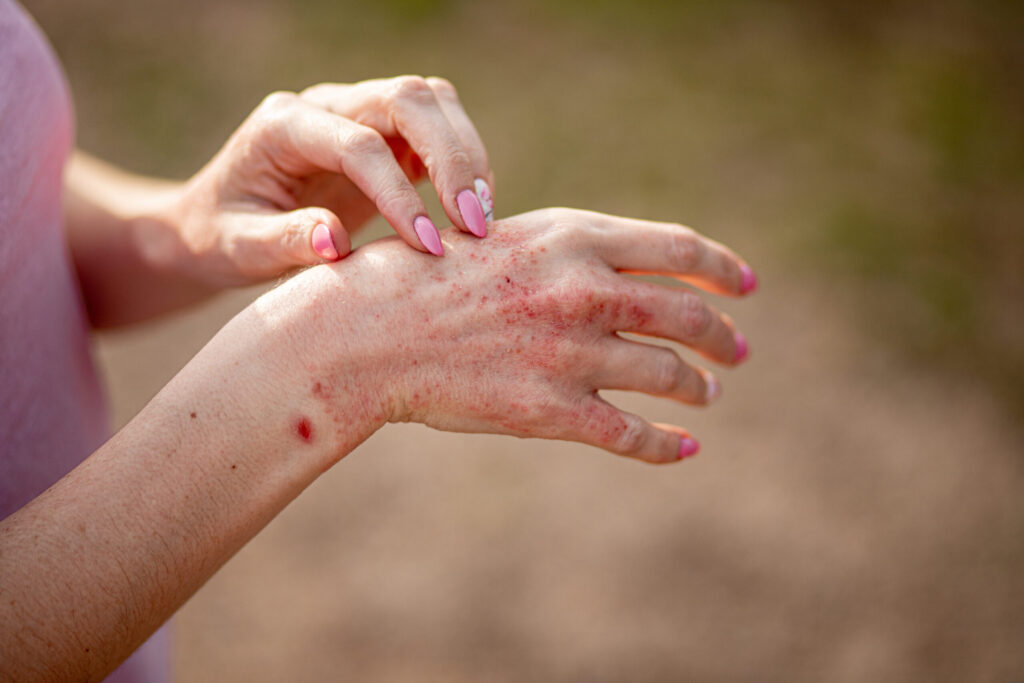
Atopic dermatitis, often called eczema, is a chronic disease that causes redness, inflammation, and irritation to the skin. Atopic dermatitis can cause your skin to get very itchy, prompting you to scratch, which leads to more irritation, swelling, and scaling.
Most people with atopic dermatitis experience flares, which are periods when the disease causes a lot of symptoms and then goes into remission, which is when the skin can clear up.
The most common symptoms of atopic dermatitis are:
- Rashes that ooze clear fluid
- Rashes that bleed
- Hardening or thickening of the skin
- Dry and red patches of skin
The causes of atopic dermatitis are still not clear. Research suggests that any changes to your skin's protective layer can make it dry. Skin dryness can then lead to itchiness and inflammation.
Problems with your immune system, exposure to certain things in your environment, and even genetic mutations can all cause changes to your protective layer of skin.
If you have a hyperactive immune system, it can create inflammation in the skin, leading to this condition. There can also be environmental triggers, like exposure to tobacco, exposure to fragrances or chemicals in skin products, and certain types of air pollutants.
Additionally, if you have a family history of atopic dermatitis, you are more likely to have the condition. This is because some genes can affect a specific protein that helps keep skin healthy, making developing atopic dermatitis more possible.
Treating atopic dermatitis
Many treatment options for atopic dermatitis exist to help you manage symptoms. Treating the condition can help you avoid potential complications like viral infections.
Topical steroid creams can keep itching under control while also helping repair your skin. In more severe cases, you may also need to take oral steroids like prednisone, which can help control inflammation.
Antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungals can help if the scratching leads to the development of an infection. For severe flare-ups, an option is to apply a topical steroid cream and then wrap the treatment area in wet dressings.
Another treatment is light therapy. During this treatment, your doctor can use controlled levels of ultraviolet light on your skin.
Managing flare-up symptoms of atopic dermatitis
If you have flare-ups, moisturize your skin at least twice daily. Look for creams, oils, ointments, or sprays that do not have fragrances or dyes. You can also use anti-itch cream to relieve the itchiness temporarily.
You will want to avoid scratching as much as possible. If your skin itches, press it instead of scratching it. You might also think about wearing gloves at night to prevent yourself from scratching while you sleep.
Taking an oatmeal bath can also be helpful. You can use colloidal oatmeal in your bath water to help lock in moisture and soothe itchy skin. Pat your skin dry, and apply a moisturizer.
It’s best not to wear tight clothing that can make itching worse. If possible, wear natural fabrics that allow your skin to breathe and that do not cause you to sweat. And if your work or home environment is too dry, try a humidifier.
Additionally, you can purchase dye and fragrance-free soaps and other skin cleansers to avoid triggering a flare-up. You may also want to take allergy medications. Antihistamines can relieve itching.
Stress and anxiety can trigger atopic dermatitis in some people, so learning stress-relieving strategies can also help prevent flare-ups.
Achieve relief from atopic dermatitis symptoms
Although atopic dermatitis is a chronic condition, there are ways you can effectively manage it and even achieve remission.
By making small changes like switching to fragrance-free body care products and exploring treatment options like creams and medications with your doctor, you can leave the discomfort of atopic dermatitis far behind.
Resource Links
- “Atopic Dermatitis in America Study Overview” via Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America
- “Atopic Dermatitis” via National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases
- “Genetics of Atopic Dermatitis: From DNA Sequence to Clinical Relevance” via National Institutes of Health
- “Oral Steroids” via National Eczema Society